Dampers – reliable components for engine damping and protection
Dampers are essential elements in engine systems where vibrations, torque peaks and resonance must be controlled. In combustion engines, the right engine damper ensures smooth operation, reduced wear, and enhanced durability. Whether in marine propulsion or stationary power generation, effective engine damping is a key factor in protecting mechanical systems and maintaining performance over time.
Function and benefits
Dampers absorb and dissipate vibrational energy generated during engine operation. A high-quality engine damper is designed to reduce rotational oscillations on the crankshaft and prevent damage from torsional forces. This results in:
- Improved engine damping and reduced vibration transmission
- Extended service life of crankshafts, gears and couplings
- Increased comfort and performance stability in engine systems
Especially in large diesel engines, dampers contribute significantly to protecting surrounding components and minimizing the risk of fatigue failure.
Types and applications of engine dampers
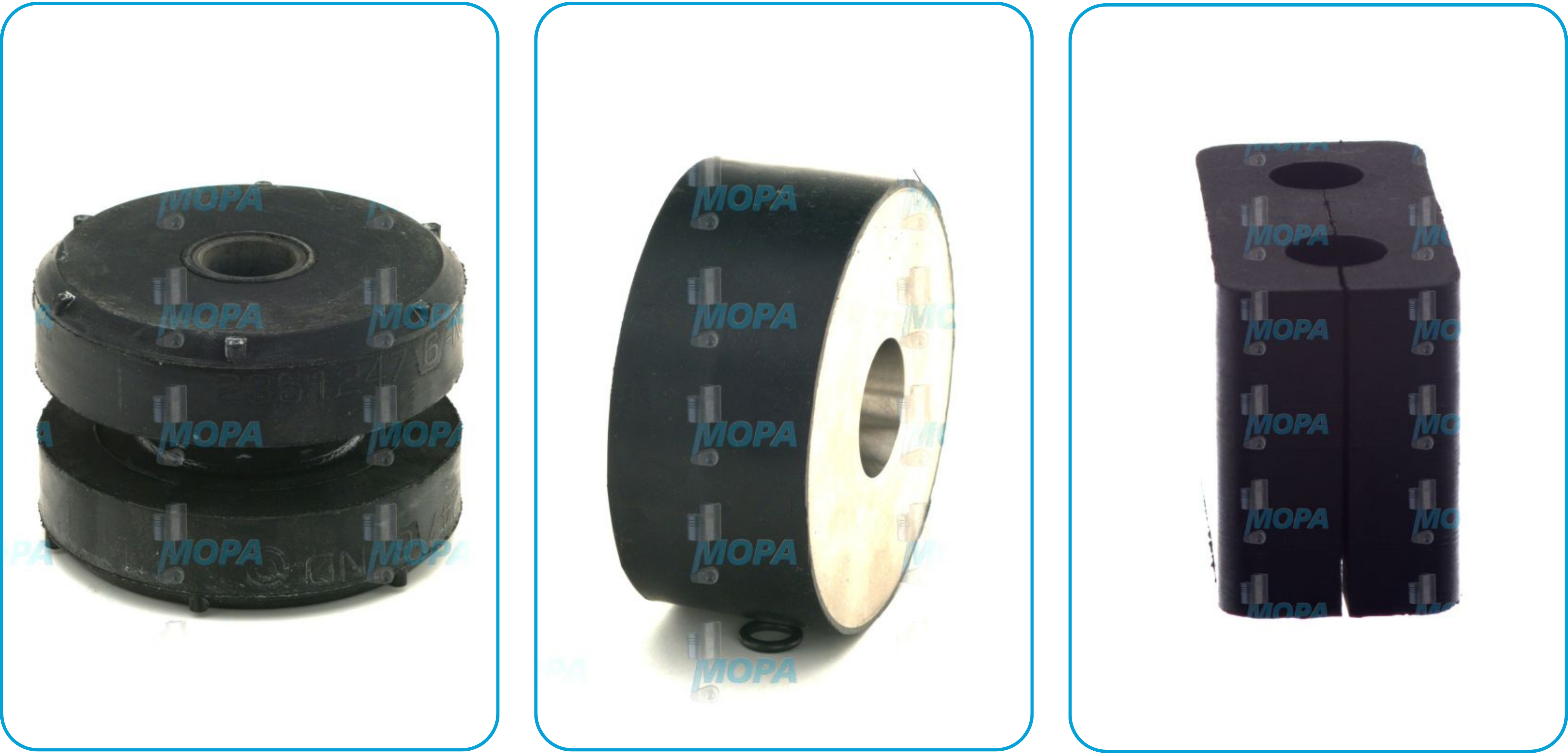
There are several types of dampers used in industrial and maritime engines. Common variants include torsional vibration dampers, viscous dampers, and rubber-based harmonic dampers. Depending on the engine size, speed range and stress profile, different damping technologies are applied.
Engine dampers are particularly important in engines with long crankshafts, such as those found in marine applications. In such setups, effective engine damping reduces resonance peaks and stabilizes rotational dynamics. Our product range includes dampers suitable for MTU, Deutz, MAN, Volvo Penta, and MWM engines.
Materials and design features
Modern dampers are made from robust materials such as steel, silicone fluid, or elastomer composites. The selection of materials depends on engine load, operating temperature and environmental influences. A well-designed engine damper must not only absorb forces but also withstand them over many operating hours.
Coatings, balancing weights and optimized internal structures are used to further improve the damping effect. In many systems, the damper is installed directly on the crankshaft pulley or between coupling elements.
Replacement and availability
Replacing engine dampers is typically part of a scheduled engine overhaul. Loss of damping performance often occurs gradually and may be indicated by increased noise, vibration or mechanical wear. It is crucial to select a damper that matches the original specifications to maintain engine damping characteristics.
We offer a wide selection of suitable dampers for marine and industrial applications. Thanks to a large local stock, we ensure fast availability and reliable delivery of OEM parts.

FAQ
What is dampers?
Dampers are mechanical devices used to absorb and control vibrations and oscillations in engine systems. In an engine context, a damper typically reduces torsional vibrations on the crankshaft to protect components and stabilize performance.
How do dampers work?
Dampers work by converting mechanical energy from vibrations into heat, which is then dissipated. Engine dampers often use viscous fluid or elastic materials to absorb torsional motion, thereby reducing oscillation amplitude and preventing resonance. This ensures smoother engine operation and protects key components from damage.