Heat exchangers for industrial and marine applications
A high-quality heat exchanger is vital for temperature regulation in internal combustion engines used in industrial facilities, marine vessels, and stationary power systems. Whether in a genset, a locomotive, or a ship’s propulsion system, maintaining optimal engine temperature is essential for performance, longevity, and emissions compliance. Reliable cooling through a heat exchanger engine setup helps protect critical components and ensures consistent operation under demanding conditions.
What is an engine heat exchanger?
An engine heat exchanger is a thermal transfer device used to dissipate excess heat from engine fluids such as coolant or oil. It operates by transferring heat from the hot fluid to another medium—typically water or air—without mixing the two substances. In marine systems, a marine engine heat exchanger often uses seawater to cool engine coolant via a closed-loop system. In land-based engines, air or fresh water may serve as the cooling medium. The function is the same: efficient and reliable thermal management.
Function and benefits of engine heat exchangers
The core function of a heat exchanger is to stabilize engine temperature by removing heat generated during combustion and operation. Effective thermal control is critical for fuel efficiency, emissions reduction, and engine durability.
- Prevents engine overheating and thermal stress
- Maintains optimal operating temperatures for fuel efficiency
- Protects seals, valves, and internal components from heat damage
- Enhances emissions performance and operational stability
A properly functioning diesel engine heat exchanger contributes significantly to overall system reliability, whether in a heat exchanger boat engine or an industrial genset.
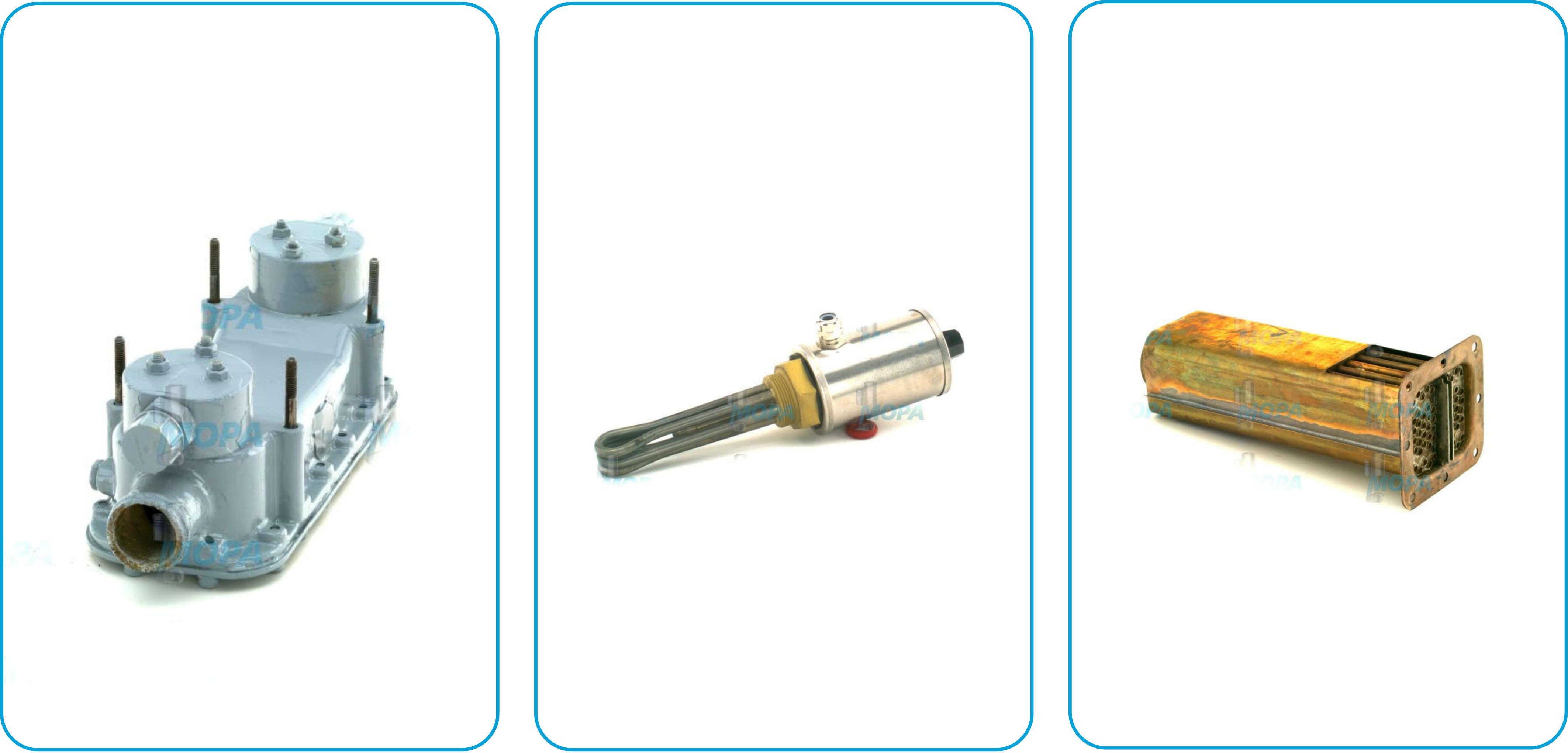
Types and materials of engine heat exchangers
There are several heat exchanger types used in industrial and marine engines, each with specific construction features and use cases.
- Shell-and-tube heat exchangers (widely used in marine and stationary engines)
- Plate heat exchangers (compact, modular units for limited spaces)
- Finned tube exchangers (common in air-cooled systems)
Materials vary depending on the medium and environment. Titanium is often used in marine engine heat exchanger systems due to corrosion resistance in seawater. Copper-nickel and stainless steel are also common, while aluminum is preferred for lightweight heat exchanger motor assemblies. The correct material ensures durability and minimal thermal resistance.
Compatibility and OEM standards
Each heat exchanger must match the engine’s thermal specifications and layout. Our components are built to OEM-equivalent standards, providing precise fit and performance. This ensures compatibility with control systems and mounting configurations across a broad range of engines.
Our portfolio includes parts suitable for engines from various manufacturers used in marine propulsion, power generation, and rail systems. OEM-equivalent quality guarantees reliability and helps extend service intervals without compromising engine integrity.
Use cases for heat exchangers
Engine heat exchangers are essential in multiple industrial sectors. In maritime applications, a heat exchanger boat engine system manages the cooling circuit using seawater without allowing contamination. In power plants, diesel engine heat exchanger units regulate large engine banks supplying base load electricity. Locomotive engines use compact, rugged exchangers to manage high-output diesel units over long distances. Each use case relies on robust thermal control to maintain operational uptime.
Buying advantages in our online shop
As a specialist in OEM-equivalent engine components, our shop offers a wide range of heat exchanger units and related accessories. B2B buyers benefit from:
- Fast delivery from EU stock and global warehouses
- Expert technical support and part identification
- User-friendly ordering and secure B2B checkout
- Large inventory including rare and high-demand parts
Whether you need a replacement heating exchanger for a marine vessel or a compact heat exchanger motor unit for a stationary generator, we provide technically vetted solutions tailored to industrial needs.
Frequently asked questions
How does a heat exchanger work?
A heat exchanger transfers heat from engine coolant or oil to another fluid (air or water) without mixing them. This protects the engine from overheating.
What is a heat exchange?
A heat exchange is the process of transferring thermal energy between two fluids. In engines, it keeps temperatures stable under load.
What is the purpose of a heat exchanger?
The main purpose is to manage excess heat, ensuring the engine runs within its optimal temperature range for performance and longevity.
How often should I clean a heat exchanger?
Cleaning heat exchanger units depends on the environment and fluid quality. Marine systems should be cleaned regularly due to salt and sediment.
Related engine components
- Gaskets
- Hoses
- Valve guides
- Springs
- Coolers
- Seals
Protect your engines and improve operational stability with our OEM-equivalent heat exchanger solutions – trusted by professionals across marine, industrial, and energy sectors.